1. Diabetes can manifest in many forms, but they all involve problems with regulating your blood sugar. There’s no cure. At its most severe, it can be life-threatening, so it’s important to understand how it works.
2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body fails to produce enough insulin. That means the main treatment is to stock up on insulin, either as an injection or through a pump.
3. You’ll often see type 1 diabetes developing in children. We don’t know exactly what causes it, though it’s likely that genetics and environment both play a factor. There’s no way to prevent yourself from getting the condition; you just have to learn to manage it.
4. If you develop diabetes later in life, it’s likely to be type 2 diabetes. This is when the insulin you do have in your body doesn’t work as it should. Metformin is normally the first choice of medication and can be taken by mouth. Taking insulin isn’t always necessary.
5. Around 90% of people with diabetes have type 2. It is most often caused by lifestyle factors, such as a lack of exercise and poor diet leading to obesity. That means that for many people, it can be avoided. Pre-diabetes is the term used for people whose lifestyle puts them at high risk of diabetes but don’t have the full-blown condition yet. It’s a warning sign.
6. There are other types of diabetes as well that are rarer and not as well-known. The most common of them is gestational diabetes, which appears during pregnancy, but there are others. Symptoms and management may vary between types.
7. Often, symptoms of diabetes can appear innocuous. Things like increased thirstiness and urination or weight loss may not ring warning bells. As the condition develops further, it may affect your vision and your body’s ability to heal wounds. Without proper treatment, symptoms will keep getting worse.
8. Some of the worst complications of diabetes include blindness, strokes, heart disease, kidney failure and poor blood flow leading to amputated limbs. Depending on the type of diabetes, you may enter a hyperglycemic state or ketoacidosis. As you can see, it’s a diverse range of complications affecting all parts of the body.
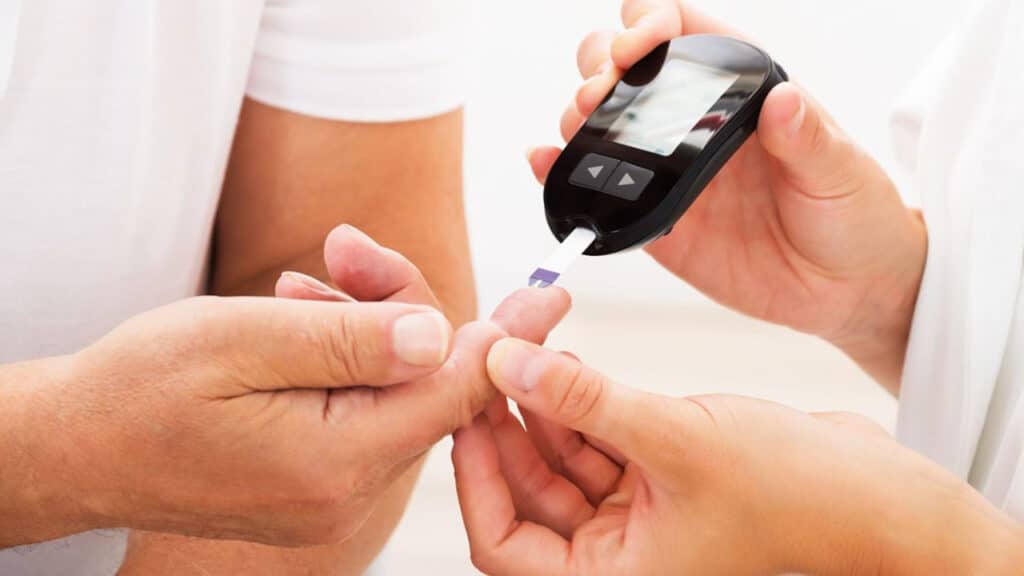
9. Testing for diabetes involves measuring the amount of glucose in the blood.
10. The quicker it is recognized and treated, the better.